1. Introduction
Swimming faster isn’t just about raw strength or endless hours of practice—it’s about refining your technique, optimizing your body’s movement in the water, and developing a smart training routine that includes everything from breathing control to mental preparation. Whether you’re an aspiring competitive swimmer or simply looking to enhance your recreational swimming experience, learning how to swim faster can help you achieve your goals in the water.
Learning how to swim faster Content Outline
| Main Sections | Subsections |
|---|---|
| 1. Introduction | – Importance of swimming speed and efficiency. – Why improving swim speed matters for both competitive and recreational swimmers. – Overview of the article’s content: 10 proven techniques. |
| 2. The Science Behind Swimming Faster | – How water resistance affects swimming speed. – Physics of swimming: drag, buoyancy, and propulsion. – Understanding the role of technique versus physical conditioning in swimming speed. |
| 3. Technique 1: Improve Body Position and Streamlining | – The importance of body position in the water. – How to maintain a horizontal and streamlined posture. – Exercises to improve core stability and body alignment. – Reducing drag by maintaining a straight line. |
| 4. Technique 2: Perfect Your Breathing | – Role of the kick in propulsion and balance. – Flutter kick vs. dolphin kick: Which is faster and when to use each?- Drills to strengthen the kick and improve timing. – Common mistakes in kicking and how to fix them. |
| 5. Technique 3: Master Your Kick | The importance of explosive starts in competitive swimming. – Proper dive technique for minimal drag and maximum speed. – Exercises to build explosive power for starts. – Improving reaction time for faster takeoffs. |
| 6. Technique 4: Focus on Arm Stroke Efficiency | – How to achieve a powerful pull with minimal energy. – Catch and pull phases: How to maximize efficiency in your stroke. – Freestyle vs. backstroke vs. butterfly stroke techniques. – Drills to improve hand positioning, pulling technique, and stroke length. |
| 7. Technique 5: Improve Your Turn and Push Off | – The importance of quick and efficient turns in pool swimming. – How to master the flip turn for freestyle and backstroke. – Techniques to improve your push-off and streamline after turns. – How to maintain momentum coming out of a turn. |
| 8. Technique 6: Enhance Your Starts and Takeoffs | – Importance of explosive starts in competitive swimming. – Proper dive technique for minimal drag and maximum speed. – Exercises to build explosive power for starts. – Improving reaction time for faster takeoffs. |
| 9. Technique 7: Strength and Conditioning Training for Speed | – The role of dryland training in improving swim speed. – Specific strength training exercises to build muscles used in swimming (e.g., shoulders, core, legs). – How plyometrics and explosive power exercises can improve starts and sprints. – Flexibility training for reducing resistance and improving stroke length. |
| 10. Technique 8: Use Swim Drills to Build Speed | – The value of drills in correcting technique flaws and building muscle memory. – Best speed-building drills for freestyle, backstroke, breaststroke, and butterfly. – Kickboard and pull buoy drills for focusing on specific aspects of your stroke. – Tips for integrating speed drills into your regular training sessions. |
| 11. Technique 9: Increase Stroke Rate and Efficiency | – Stroke rate vs. stroke length: Striking the right balance for speed. – How to improve turnover without sacrificing technique. – Using tempo trainers and swim metrics to monitor progress. – Drills to improve stroke rate and maintain stroke efficiency. |
| 12. Technique 10: Mental Strategies for Faster Swimming | – The role of mental focus and visualization in competitive swimming. – How to use goal-setting and positive affirmations to enhance performance. – Dealing with performance anxiety and maintaining calm under pressure. – Mental training techniques for sustaining motivation and pushing limits during races. |
| 13. Nutrition and Hydration for Peak Swimming Performance | – How proper nutrition can support energy levels and muscle recovery. – Pre-swim and post-swim meals for sustained energy. – Importance of staying hydrated before, during, and after training or races. – Nutritional tips for improving endurance and speed. |
| 14. How to Track and Measure Your Progress | – Using swim trackers and metrics to monitor speed improvements. – How to set measurable goals for improving swimming speed. – Frequency and types of swim tests to track your progress. – Adjusting your training plan based on your progress. |
| 15. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) | – Q1: How long does it take to swim faster? – Q2: What is the most important technique for swimming faster? – Q3: Do I need to swim more often to improve speed? – Q4: Should I focus on stroke rate or stroke length to swim faster? – Q5: How can I swim faster without getting tired? – Q6: What equipment can help me improve my swim speed? |
| 16. Conclusion | – Recap of the 10 techniques for swimming faster. – Encouragement to implement these techniques consistently to see improvement. – Final motivational call to action: Push your limits and enjoy your progress as a faster swimmer. |
Overview of the Article’s Content: 10 Proven Techniques
In this article, we’ll explore 10 proven techniques to improve your swim speed, backed by expert advice and practical exercises. From streamlining your body position to perfecting your turns and starts, we’ll guide you through the process of swimming faster, more efficiently, and with better endurance.
2. The Science Behind Swimming Faster
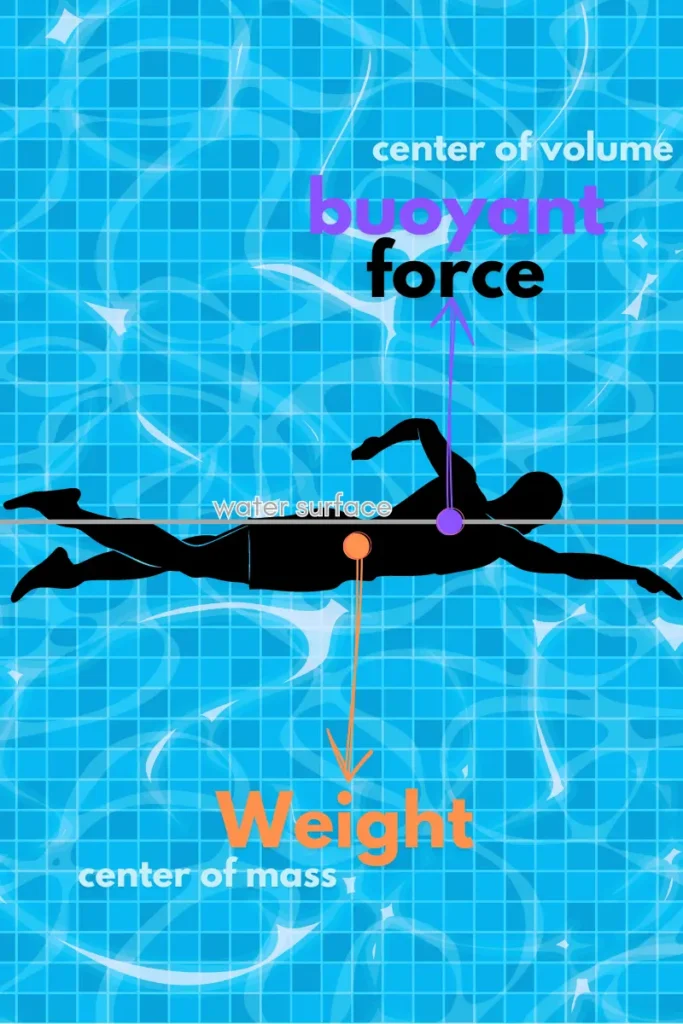
Before diving into specific techniques, it’s essential to understand the science behind swimming faster. Swimming involves propelling your body through water—a medium that creates a significant amount of resistance. Thus, to swim faster, you must work to minimize this resistance and maximize propulsion.
The Role of Drag and Buoyancy
Water is nearly 800 times denser than air, which means every movement in the water is met with resistance. Consequently, swimmers face two types of drag: frontal drag, which comes from moving through the water, and turbulent drag, caused by the water swirling around them as they swim.
To reduce drag, it’s crucial to maintain a streamlined body position and minimize unnecessary movements. Proper buoyancy also plays a role in how efficiently you can glide through the water. By staying balanced and maintaining a flat, horizontal position, you reduce the surface area that’s exposed to water resistance.
Propulsion and Speed
Your body’s propulsion in water comes from a combination of arm strokes, kicks, and the force you generate from your core. Therefore, to maximize propulsion and swim faster, you need to perfect each part of your stroke and kick. A more efficient stroke requires less energy and produces more speed.
3. Improve Your Body Position to Swim Faster
One of the most crucial elements of swimming faster is improving your body position in the water. A streamlined, horizontal position reduces drag and allows you to move more efficiently.
Streamlining Your Body for Speed
The key to a fast swim is a straight, streamlined body position. This means your head, hips, and feet should be aligned as much as possible. To avoid letting your legs sink, or your head lift too high out of the water, focus on maintaining drag-free alignment.
To improve your body position:
- Engage Your Core: A strong core helps keep your body aligned. Focus on activating your abdominal and lower back muscles as you swim.
- Head Position: Keep your head in a neutral position, with your eyes looking down. Avoid lifting your head too high, as this can cause your hips to drop.
- Hips and Legs: Keep your hips near the surface of the water to maintain horizontal alignment. Kicking from your hips rather than your knees will help keep your legs afloat and reduce drag.
Drills for Better Body Position
Practicing the Superman glide drill can help you work on body alignment. Push off from the wall with your arms stretched out in front of you and your body in a straight line. Focus on maintaining a flat, streamlined position without kicking. This will train your body to stay aligned and reduce drag.
4. How to Swim Faster by Perfecting Your Breathing Technique
Proper breathing is often overlooked, but it is critical for swimming faster. Poor breathing can throw off your rhythm, causing you to lose momentum and disrupt your stroke. Learning to breathe efficiently will help you maintain speed and endurance.
Bilateral Breathing for Balance
One technique that can significantly improve your speed is bilateral breathing, which means breathing on both sides. Breathing every three strokes rather than two allows for a more balanced stroke and better body alignment. Additionally, it prevents over-rotation, which can slow you down.
Timing Your Breaths
In freestyle, the timing of your breaths is key to maintaining your speed. Aim to inhale quickly as you rotate your head to the side and exhale steadily while your face is in the water. Try not to pause or hold your breath, as this can interrupt your stroke.
Drills for Breathing Control
Practice single-arm drills where you swim with one arm while keeping the other extended in front of you. Focus on smooth, controlled breathing as you move through the water. This helps build the habit of maintaining a steady rhythm while breathing.
5. Master Your Kick to Swim Faster
The kick is essential to swimming faster, as it provides propulsion and helps maintain body position. However, an efficient kick can save energy by adding more speed.
Efficient Kicking Techniques
The most effective kick in freestyle is the flutter kick. It involves small, quick movements powered by your hips rather than your knees. A common mistake swimmers make is bending their knees too much, which causes drag and reduces propulsion.
Powerful Kicks for Sprinting
Sprinters need a faster and more powerful kick. Focus on developing strong leg muscles through targeted dryland exercises, like squats and lunges and in-water kicking drills.
Drills for a Faster Kick
Using a kickboard is one of the best ways to isolate your kick and improve its speed and efficiency. Incorporate kick sets into your workouts, using both flutter and dolphin kicks, and aim to increase the speed and intensity over time.
6. Focus on Arm Stroke Efficiency to Swim Faster
Your arm stroke is the primary source of propulsion in swimming, so improving your technique here can make a huge difference in your speed.
The Catch and Pull Phases
To swim faster, you need to perfect the catch and pull phases of your stroke. The catch occurs when your hand enters the water and “grabs” it, while the pull phase involves pushing the water back to propel yourself forward. A strong, efficient pull uses your entire arm, from fingertips to forearm, to create maximum propulsion.
Reducing Drag in the Recovery Phase
The recovery phase is when your arm comes out of the water to return to the starting position. To minimize drag, keep your elbows high and move your hand forward smoothly, avoiding wide arcs or flailing movements.
Drills for Better Arm Stroke
One of the best drills for improving your arm stroke is the catch-up drill. Swim freestyle, but only pull with one arm at a time, allowing the other arm to remain extended in front of you. This helps you focus on the individual mechanics of each stroke.
7. Improve Your Turn and Push-Off for Faster Pool Swimming
Turns are one of the most critical moments in pool swimming, where you can either gain or lose valuable time. A quick and efficient turn can make a significant difference in your overall speed.
Mastering the Flip Turn
The flip turn is the fastest turn technique for freestyle and backstroke. To execute it properly, swim toward the wall, tuck your chin to your chest, and initiate a quick somersault as you approach. Plant your feet on the wall and push off in a streamlined position.
Improving Your Push-Off
After the turn, your push-off should be explosive and streamlined. Keep your arms extended in front of you, and stay underwater for as long as possible, using a dolphin kick to maintain speed.
Drills for Faster Turns
Incorporating turn practice into your workouts can help you develop a more efficient flip turn. Start by performing slow-motion flips to practice the movement, then gradually increase speed as you become more comfortable.
8. Enhance Your Starts for Explosive Speed
A good start can set the tone for the rest of your race. In sprint events, especially, a fast and powerful start can be the difference between winning and losing.
Dive Technique for Competitive Starts
Focus on your dive technique to improve your start. Begin with a strong push off the block, aiming for minimal splash and drag as you enter the water. Your arms should be extended, and your body should remain streamlined as you dive.
Building Power for Faster Starts
Strength training can help improve your explosive power off the block. Exercises like box jumps, squats, and plyometrics are particularly effective for building the leg strength needed for a powerful start.
Drills for Starts
Practice track start drills where you focus on your reaction time and push-off speed. Time your starts to track your progress and aim for quicker takeoffs.
9. Strength and Conditioning Training to Swim Faster
Dryland training is crucial for improving swim speed. By building strength in key muscle groups, you can enhance your power and endurance in the water.
Targeted Strength Exercises
To swim faster, you need to focus on strengthening the muscles that contribute to propulsion, including the shoulders, back, core, and legs. Effective exercises include:
- Pull-ups: Strengthen your shoulders and back.
- Planks: Improve core stability for better body alignment.
- Squats and Lunges: Build leg strength for a stronger kick.
Plyometric Training for Explosiveness
Plyometrics, or explosive power exercises, are particularly beneficial for sprinters. Box jumps, medicine ball throws, and clap push-ups help improve your ability to generate power quickly, which is essential for starts and turns.
10. Use Swim Drills to Build Speed and Efficiency
Swim drills are essential for refining your technique and building speed. Drills help you focus on specific aspects of your stroke and improve muscle memory, leading to more efficient swimming.
Speed-Building Drills for Freestyle
Incorporating drills like sprint intervals and fist drills can help improve your stroke speed and power. Sprint intervals involve alternating between fast and slow swimming to build endurance and speed. For example, swim 25 meters as fast as you can, followed by 50 meters at a slower pace to recover, and repeat the cycle.
Drills for Specific Strokes
If you swim more than just freestyle, drills tailored to each stroke are essential. For backstroke, try the double-arm drill to improve stroke coordination; this involves using both arms simultaneously to enhance your rhythm and timing. For butterfly, single-arm butterfly drills help you focus on maintaining rhythm and technique while reducing fatigue.
Additionally, incorporating drills that emphasize kick and body position can enhance overall efficiency. For example, performing vertical kicks helps build leg strength and improves your kick’s power while isolating your legs for focused training.
Integrating Drills into Training Sessions
To get the most out of your swim drills, integrate them into your regular training sessions. Allocate specific times during your practice for drills, alternating between technique-focused sessions and endurance or speed work. This balanced approach helps reinforce good habits while gradually building speed and efficiency in the water.
11. Mental Strategies for Faster Swimming
Your mindset can significantly impact your performance in the pool. Developing mental strategies like goal-setting, visualization, and positive self-talk can help you swim faster by improving your focus and confidence.
Visualization for Success
Many swimmers use visualization techniques to mentally rehearse their races. By picturing yourself swimming with perfect technique and winning your race, you can improve your confidence and reduce anxiety. Visualization can also help you prepare for different race scenarios, allowing you to strategize and adapt effectively during competition.
Dealing with Pre-Race Nerves
Performance anxiety can slow you down, especially in competitions. Techniques like deep breathing, meditation, and focusing on your own race can help you stay calm and focused. Consider practising mindfulness exercises before training sessions or competitions to enhance your mental resilience.
12. Nutrition and Hydration for Peak Swimming Performance
To swim faster, you need to fuel your body properly. Nutrition plays a vital role in providing the energy and nutrients required for muscle function and recovery.
Pre-Swim Nutrition
Before a swim workout or race, eat a meal rich in complex carbohydrates and lean protein to fuel your muscles. Avoid heavy or fatty foods that can slow you down in the water. A banana or a small bowl of oatmeal with fruit can provide the necessary energy without weighing you down.
Post-Swim Recovery
After a swim session, focus on replenishing your body with protein to aid in muscle recovery and carbohydrates to restore glycogen levels. Staying hydrated is also essential, as dehydration can significantly impair performance. Drinking water or an electrolyte drink can help maintain optimal hydration levels.
13. How to Track Your Progress in Swimming
Tracking your progress is key to improving your speed over time. Use swim trackers or apps to measure your stroke rate, distance, and lap times. By analyzing this data, you can identify areas for improvement and adjust your training accordingly.
Setting Measurable Goals
Set specific, measurable goals for your swim speed. For example, aim to reduce your 100-meter freestyle time by 2 seconds over a month. Setting incremental goals not only keeps you motivated but also allows you to celebrate small victories along the way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: How long does it take to swim faster?
It depends on your starting point and the consistency of your training. With regular practice and proper technique, most swimmers see noticeable improvements within a few weeks to a few months.
Q2: What is the most important technique for swimming faster?
Body position is the foundation of swimming fast. A streamlined position reduces drag and helps you move more efficiently through the water.
Q3: Do I need to swim more often to improve my speed?
Swimming more often can help, but it’s important to balance frequency with proper technique. Swimming with poor form can reinforce bad habits, so focus on quality over quantity.
Q4: Should I focus on stroke rate or stroke length to swim faster?
Finding the right balance between stroke rate and stroke length is crucial. Increasing stroke rate without sacrificing technique can lead to improved speed. Experiment with different combinations to see what works best for you.
Q5: How can I swim faster without getting tired?
Focus on improving your technique and building endurance. Incorporate drills that emphasize efficiency and ensure you’re following a well-structured training program that allows for adequate rest and recovery.
Q6: What equipment can help me improve my swim speed?
Consider using swim fins, paddles, and kickboards during practice. These tools can help strengthen your strokes and kicks while providing valuable feedback on your technique.
Conclusion:
Learning how to swim faster requires a combination of improving your technique, building strength, and staying mentally sharp. By implementing the 10 proven techniques outlined in this article—from perfecting your body position to refining your starts—you can significantly improve your swim speed and efficiency. Remember, consistency and patience are key. Keep pushing your limits, and you’ll soon see progress in the pool.